Albumin and Edestin
What is Albumin
Albumin is the main blood protein found in blood plasma. It is primarily used by the body to transport various nutrients or drugs and also to maintain oncotic pressure and balance in the internal environment.
If an acute condition occurs and the body cannot obtain basic building blocks for the production of body proteins in a standard way, it begins to obtain them from Albumin.
However, this can quickly lead to a significant disruption of the body’s internal environment (homeostasis), which can result in rapid organ failure.
What is Edestin?
It bears a striking resemblance to Albumin. For several decades, scientists have been interested in the interchangeability of these proteins, especially in medicine.
Together with the German company HealChain GmbH, we have conducted an exhaustive analysis of what the global professional community knows about Edestin. We used the Ontosight platform, which works with artificial intelligence. We mapped the results of more than 92,000 expert studies. This gives us a detailed overview of Edestin’s known properties.
![]()
We have verified that there is no other research team or organization worldwide that is dedicated to the development or preparation of blood plasma substitute from Edestin. Therefore, our project is unique and we are exceptional in this area. Our work is not only pioneering but also entirely original.

Edestin Structure
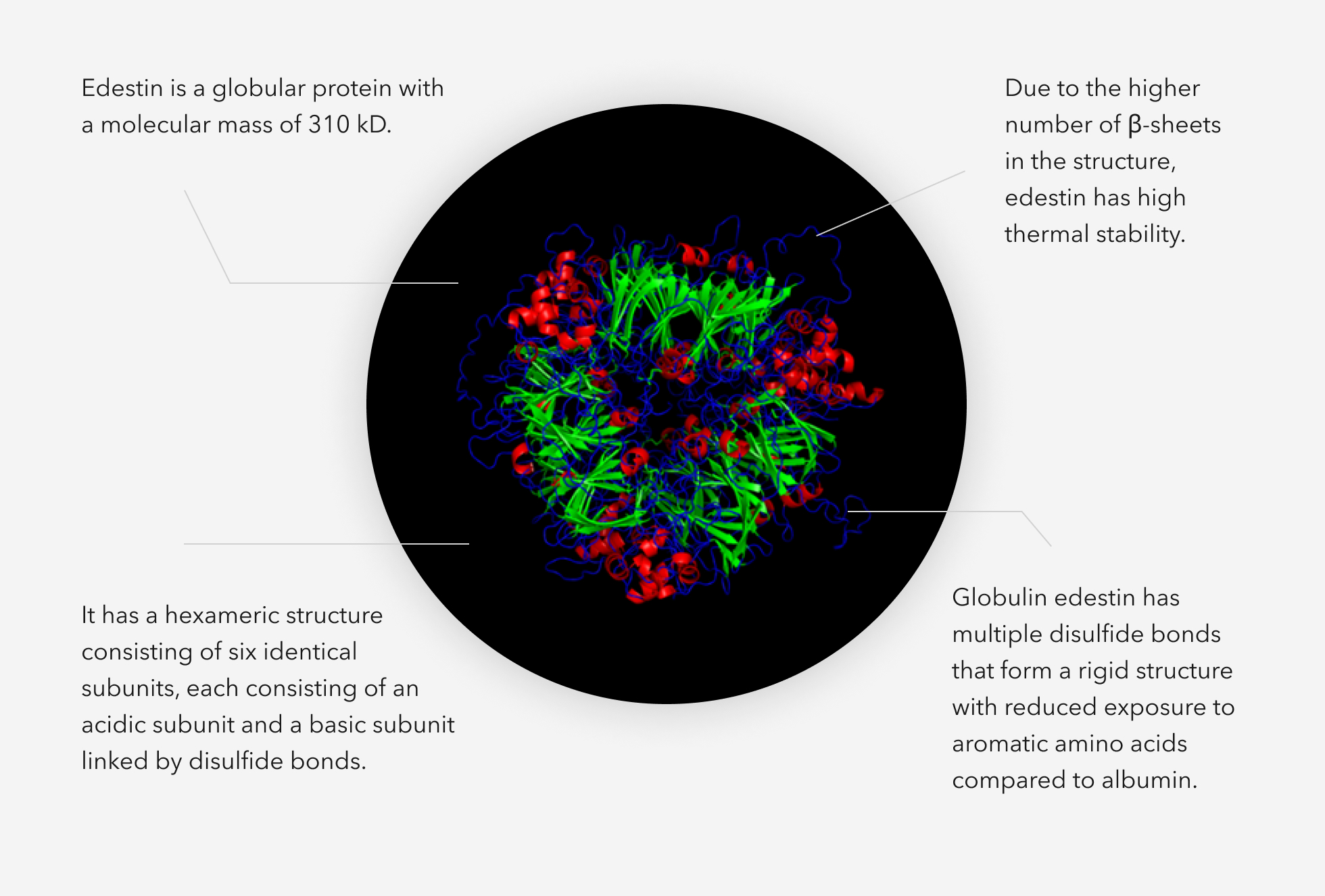

Edestin Types
There are three types of edestin. We refer to them as edestin1, edestin2, edestin3. The antigenic sites of edestin1 are more accessible than those of edestin2, while the antigenic sites of edestin3 are inaccessible to antibodies. Albumin and edestin3 are more immunologically compatible.
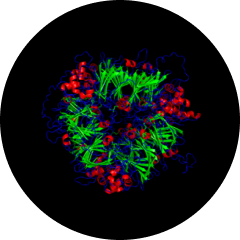
edestin 1
(511 AA)
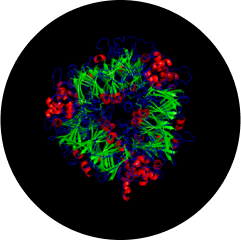
edestin 2
(491 AA)
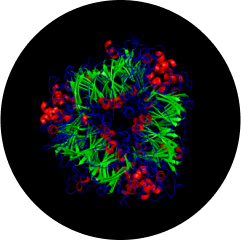
edestin 3
(493 AA)
- Alpha helix
- Beta sheets
- Helix
Albumin vs. Edestin

albumin
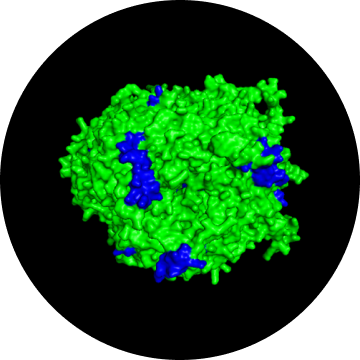
edestin1
- Antigenic sites